Day04 - Python基本语法 Part 1
今天开始将进行Python基本语法练习,因大部分语法跟很多程序语言相似,故这个部分将主要以笔记方式注记重点,做为未来的备忘录。
补充说明:部分范例程序来自於W3Schools。
Python特色
- 直译式语言,不需要事先编译。
- 可读性高,更接近於一般英文语句。
- 使用换行符号区隔指令。 (大部分程序语言多使用「;」做结尾)
- 使用空格界定范围。 (大部分程序语言多使用括号界定范围)
if 2>1:
print("2>1")
print("First Part")
else:
print("Else Part")
注解
- 单行注解
#This is a comment
- 多行注解
"""
Comment 1
Comment 2
Comment 3
"""
变数
- 变数型态依指派的资料型态而定
- 显示变数型态
x = 4
y = "Test"
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
- 变数型态会依後续指派的数值型态自动转变
x = 4
print(type(x))
x = "Test"
print(type(x))
- 指派时宣告型态
x = str(1)
print(type(x))
x = int(1)
print(type(x))
x = float(1)
print(type(x))
- 一次指派多个变数不同的值
x, y, z = "A", "B", "C"
- 一次指派多个变数相同的值
x = y = z = "A"
- 将数值集合拆分指派至多个变数
testSet = ["A","B","C"]
x, y, z = testSet
资料型态
-
Text Type:str
-
Numeric Types:int, float, complex
x = 1 # 数值
y = "j" # 文字
z = 1j # 复合型态
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
- Sequence Types:list, tuple, range
x = ["A","B","C"] # list
y = ("A","B","C") # tuple
z1 = range(1, 7) # range
z2 = range(7) # range
- Mapping Type:dict
employee = {"id": 1, "name": "Alice"}
print(employee)
print(employee["name"])
- Set Types:set, frozenset
x = {"A","B","C"} # set
x = frozenset({"A","B","C"}) # frozenset
- Boolean Type: bool
x = True
y = False
使用bool()可以将各种型态的变数转换为bool型态。
判断为False的情境:
- 文字:空字串
- 数字:0
- 集合:空集合
- Binary Types:bytes, bytearray, memoryview
乱数
需要使用Random模组
import random
print(random.randrange(1,10))
字串处理
因重点较多故另外整理出来。
- 多行字串指派:使用"""或'''都可以
x = """Line 1.
Line 2.
Line 3.
"""
y = '''Line 4.
Line 5.
Line 6.
'''
print(x)
print(y)
- 字串长度
a = "Test"
print(len(a))
- 判断字串是否存在於另一个字串
x = "Hello World"
print("World" in x)
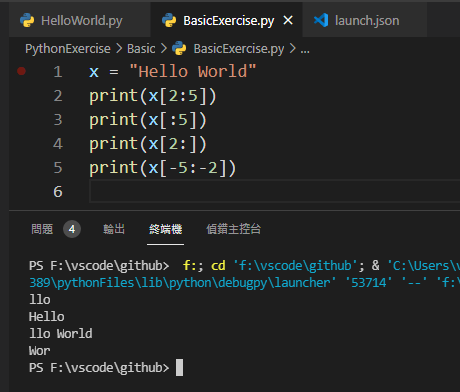
- 取出子字串
以矩阵中的指标范围处理,写法:array[startIndex:endIndex]。
注意:endIndex不包含在选取范围内
x = "Hello World"
print(x[2:5])
print(x[:5])
print(x[2:])
print(x[-5:-2])
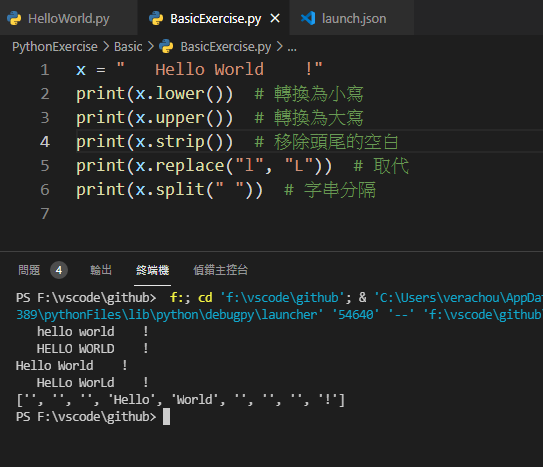
- 字串修改
x = " Hello World !"
print(x.lower()) # 转换为小写
print(x.upper()) # 转换为大写
print(x.strip()) # 移除头尾的空白
print(x.replace("l", "L")) # 取代
print(x.split(" ")) # 字串分隔
- 字串合并
x = "Hello "
y = "World"
z = x + y
print(z)
- format
因字串和数字不能以「+」直接合并,可透过format的写法,让数值变数取代该字串中特定位置,以达到字串和数字合并的效果。
quantity = 3
itemno = 567
price = 49.95
myorder = "I want {} pieces of item {} for {} dollars."
print(myorder.format(quantity, itemno, price))
可以使用index来指定欲取代的变数。
quantity = 3
itemno = 567
price = 49.95
myorder = "I want to pay {2} dollars for {0} pieces of item {1}."
print(myorder.format(quantity, itemno, price))
Arduino 扩充版 W5100 - EEPROM 烧录
Arduino W5100 是一块含有网路及EEPROM功能的扩充版. 笔者在之前的文章中曾提过可以...
【後转前要多久】# Day11 CSS - 区块元素、行内元素
为了让元素的边界格线看得更清楚, 这边统一对<body>之外的所有元素加上outline...
Day23:交给专业的来
我们来看看Executor介面的内容: package java.util.concurrent; ...
day 28 - 请问, 有流程图可以看吗?
『请问, 有流程图可以看吗?』每次我看别人的系统时, 都会想这样问 身为一个需要透过视觉来辅助理解的...
Day36 参加职训(机器学习与资料分析工程师培训班),网站设计与网页工程技术
上午: 网站设计与网页工程技术 # 连接资料库 import sqlite3 import nump...