Day 23. slate × Operation × L-transform
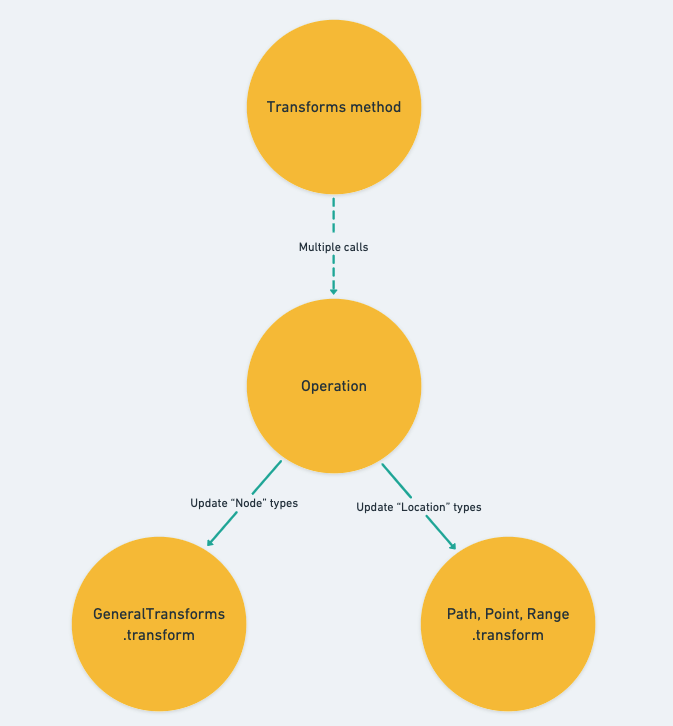
上一篇文章我们深入了解了 Operation 的 transform function 是如何实作针对各种不同的 Operation types 的更新功能的,并略过了一切关於 Location type 的更新相关的内容。包含 selection 的主要更新逻辑也一样,我们只提到了它们是交由各自对应到的 transform method api 来处理,它们分别是:
-
Path.transform -
Point.transform -
Range.transform
我们在 Day 18 时就有先剪短提到过这几个 methods 的功用了,它们同时负责 Location value 的更新以及确保存在於编辑器里的 Locations 都是 Immutable 的。
基本上整个编辑器就是仰赖前一篇介绍的 transform function 以及今天的这三个 transform method apis 作为资料更新最底层的功能,就像是盖房子一样,其他如 Operations 或是最 high-level 的 Transform methods 都只是基於它们再向上搭建另外一层功能而已
前一篇是介绍 Node types 的更新,相信今天的任务是什麽就不用多赘述了 ?
Path.transform
这个 method 主要需要传入两个参数,分别是 path 、 operation 。
-
path:主要传入接受更新的路径资料,会因应传入的 operation 回传相对应更新过後的 Immutable value 。 -
operation:执行的 Operation 资料,下方的内容会很常取出在operation.pathalias 为op使用,之後在这个小节看到op代表的就是operation.path的 value 。
还有一个 options.affinity ,我们在後续遇到它的使用情境时再介绍它的功用
/**
* Transform a path by an operation.
*/
transform(
path: Path,
operation: Operation,
options: { affinity?: 'forward' | 'backward' | null } = {}
): Path | null {
return produce(path, p => {
// ... Path.transform implementation
});
}
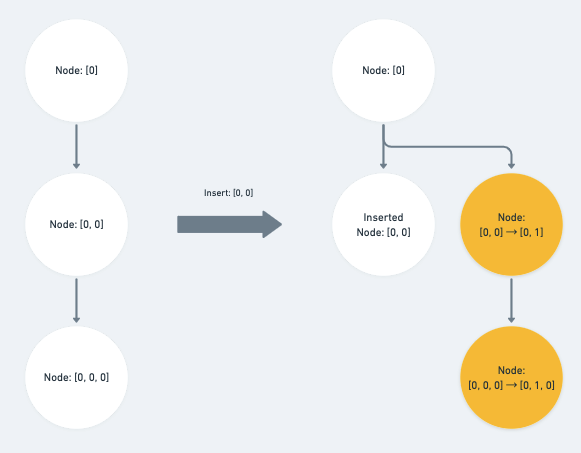
insert_node
会受到『插入节点』所影响的路径就只有三种:
- 完全相同的路径
- 同层且位於 op 之後的 sibling 的路径
- op 为祖先之路径
做的操作一样都是将 path 阵列里与 op index 同层的值 + 1
case 'insert_node': {
const { path: op } = operation
if (
Path.equals(op, p) ||
Path.endsBefore(op, p) ||
Path.isAncestor(op, p)
) {
p[op.length - 1] += 1
}
break
}
-
- 容易懂,插入的节点位於同一层又在它的位置以前,所以要将自己的 index + 1。
-
就稍嫌 tricky 一点了,注意到它指定 + 1 的阵列 index 是
op的 index 值,所以如果今天插入的节点路径是位於path上方的祖先时,我们会将与opindex 同层的值 + 1 ,因为是它祖先那一层被异动到
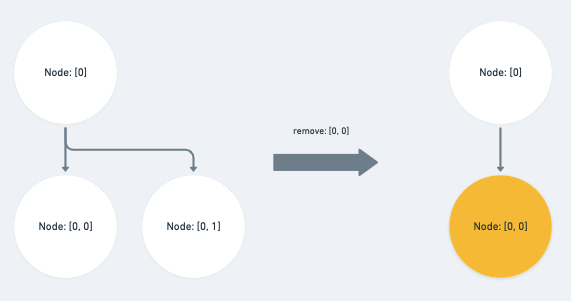
remove_node
将与『被删除的节点』相同,或位於它子层的路径直接删除。
case 'remove_node': {
const { path: op } = operation
if (Path.equals(op, p) || Path.isAncestor(op, p)) {
return null
}
// ... else if statement
break
}
如果被删除的节点路径位於 path 之前的 sibling 的话则将 index 的值 - 1
else if (Path.endsBefore(op, p)) {
p[op.length - 1] -= 1
}
merge_node
『合并节点』可以分为两种情形:
-
op 与 path 相等,或为 path 之前的 sibling :
直接将 path 对应的 index 值 - 1
case 'merge_node': { const { path: op, position } = operation if (Path.equals(op, p) || Path.endsBefore(op, p)) { p[op.length - 1] -= 1 } // ... else if statement break } -
op 为 path 的祖先路径:
除了将对应的 index 值 -1 之外,我们还需要子层的 index 值去加上
position,也就是它前一个 sibling 的 index 值else if (Path.isAncestor(op, p)) { p[op.length - 1] -= 1 p[op.length] += position }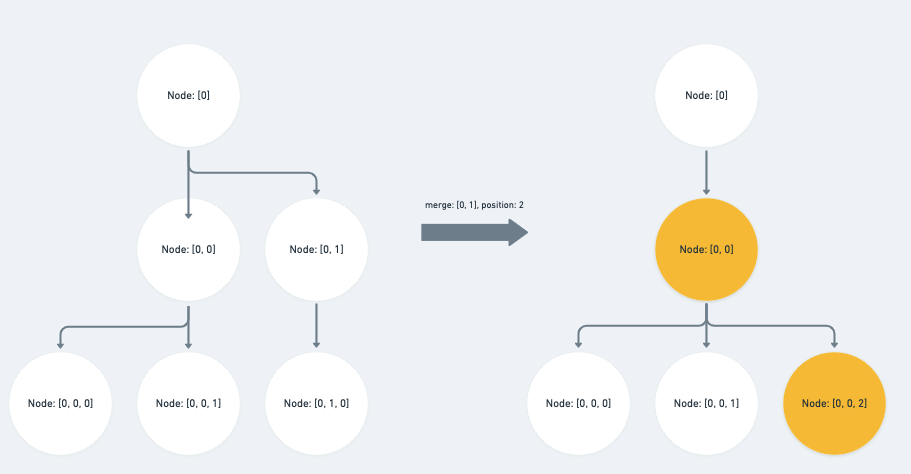
split_node
『拆分节点』可以分为三种情形:
-
op与path相等这里就会受到
options.affinity所影响了,affinity在这里代表的是将原始的path指向的节点向後( forward )或是向前( backward )做拆分,如果是向後拆分则将原始路径的 index + 1 ,向前则不需要做任何操作。case 'split_node': { const { path: op, position } = operation if (Path.equals(op, p)) { if (affinity === 'forward') { p[p.length - 1] += 1 } else if (affinity === 'backward') { // Nothing, because it still refers to the right path. } else { return null } } // ... other statements break }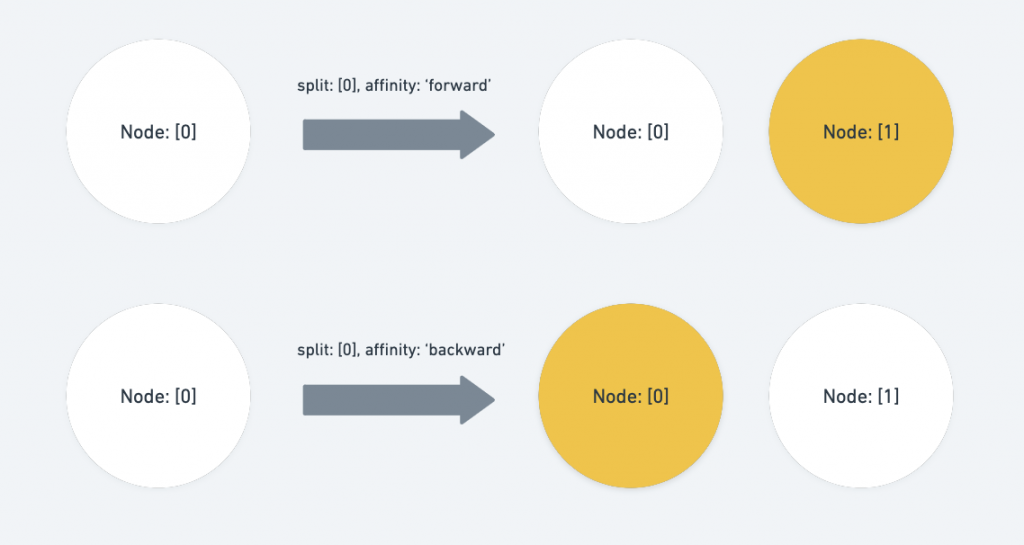
-
op与path同层,并位於path前面的 sibling直接将 path 的 index 值 + 1 。
else if (Path.endsBefore(op, p)) { p[op.length - 1] += 1 } -
op为path的祖先,且opindex 的子层对应到的pathindex 位於position的後方:同层的 index 值 + 1 ,同时子层节点扣除掉拆分的 position offset
else if (Path.isAncestor(op, p) && path[op.length] >= position) { p[op.length - 1] += 1 p[op.length] -= position }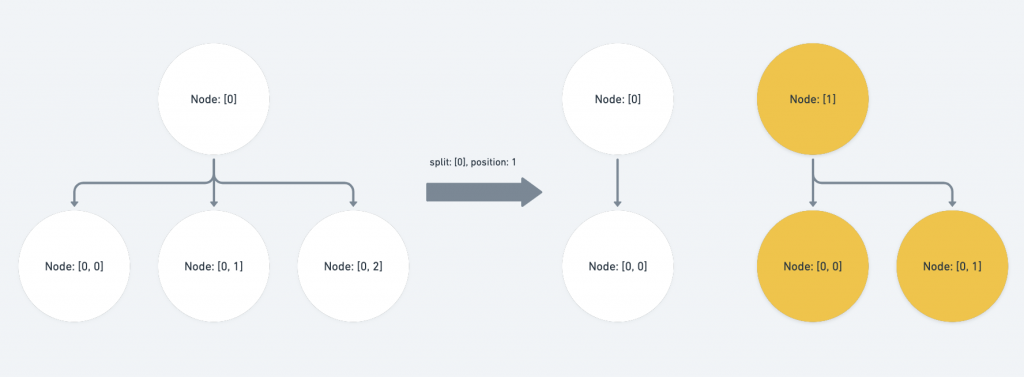
move_node
首先挡掉了 no-op ,也就是不用执行任何操作,新旧路径皆相等的情形
case 'move_node': {
const { path: op, newPath: onp } = operation
// If the old and new path are the same, it's a no-op.
if (Path.equals(op, onp)) {
return
}
// ... If else implementations
break
}
接着拆分成四种情形去探讨:
-
op( Operation 里欲移动的旧路径 )为p的祖先或op与p的路径相等:此时的
p被包含在 Operation 的搬迁范围内,我们要将onp( Operation 里欲移动到的新路径 )补上opindex 之後、p所涵盖到的子层。if (Path.isAncestor(op, p) || Path.equals(op, p)) { const copy = onp.slice() // ... if statement for the edge case return copy.concat(p.slice(op.length)) }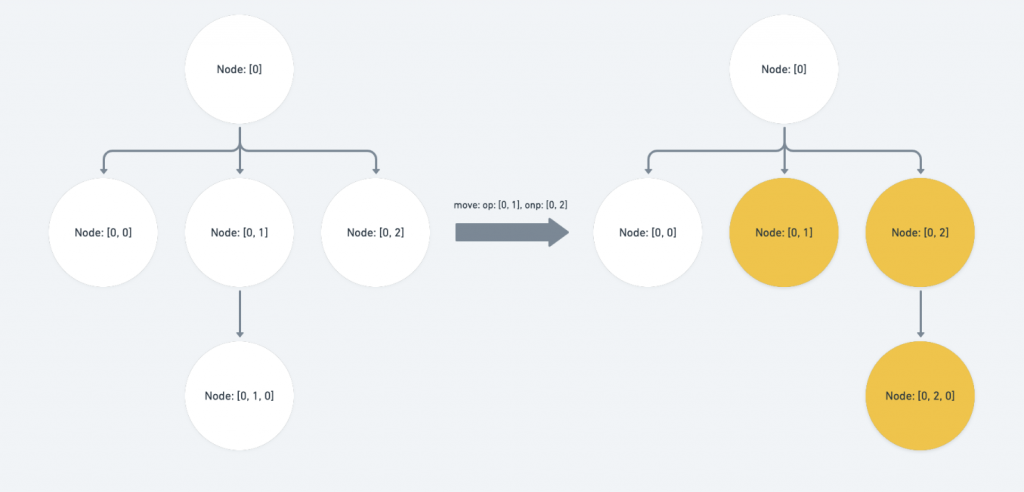
上图的结果就是:
[0, 2]会向前调动到[0, 1],而[0, 1]的整个 branch 则会一起向後移动一个 sibling 。再来这个情形还有一个 edge case 是需要注意的,也就是当
op位於onp之前,同时为onp的上层路径。此时我们会需要调整
onp於op层的 index value 将它 -1 ,因为op会遭到移除if (Path.endsBefore(op, onp) && op.length < onp.length) { copy[op.length - 1] -= 1 }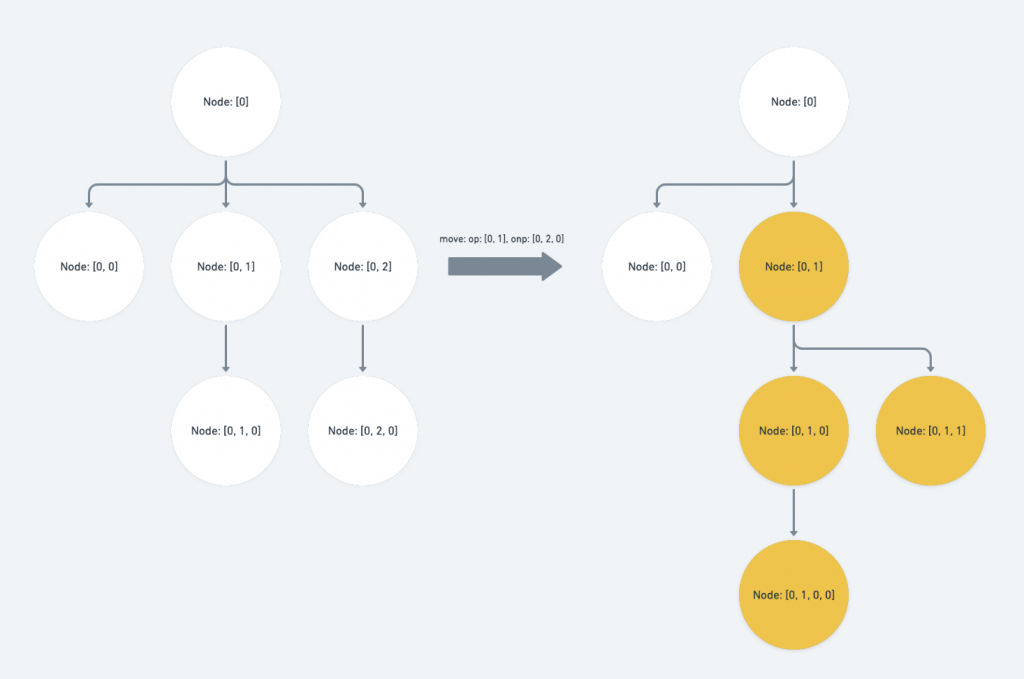
-
op与onp同层,且onp为p的祖先或onp与p的路径相等:此时我们需要调整
p於opindex 层的 value 。如果 op 位於 p 之前,代表移动後 value 会因为该层前面的 sibling 遭到拔除因而需要 -1 ;反之则代表该层会有新的 sibling 被移动到前面因而需要 +1else if ( Path.isSibling(op, onp) && (Path.isAncestor(onp, p) || Path.equals(onp, p)) ) { if (Path.endsBefore(op, p)) { p[op.length - 1] -= 1 } else { p[op.length - 1] += 1 } }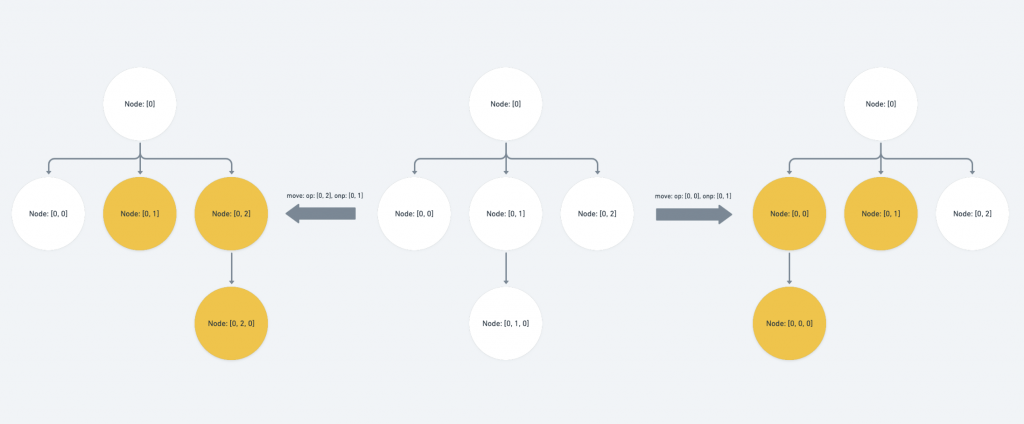
-
onp位於p之前,或onp与p相等,或onp为p之祖先:代表我们要将某一组路径搬迁到
p之前,因此我们需要将p於onpindex 层的 value +1else if ( Path.endsBefore(onp, p) || Path.equals(onp, p) || Path.isAncestor(onp, p) ) { // ... if statement for the edge case p[onp.length - 1] += 1 }
需要注意的 edge case 为:如果要搬迁的
op位於p之前,代表会有一组路径从p之前的位置受到搬迁,我们需要扣除p於op层的 index valueif (Path.endsBefore(op, p)) { p[op.length - 1] -= 1 } -
op位於p之前:代表我们要将某一组路径从 p 之前搬迁走,因此我们需要将
p於opindex 层的 value -1else if (Path.endsBefore(op, p)) { if (Path.equals(onp, p)) { p[onp.length - 1] += 1 } p[op.length - 1] -= 1 }
这里 If statement 的内容笔者也不太确定,照理来说
Path.equals(onp, p)应该已经在前一组 else if 中被筛掉了才对。欢迎在下方留言补充!
Point.transform
主要需要传入两个参数,分别是 point 、 op 。
-
point:主要传入接受更新的 Point 资料,会因应传入的 operation 回传相对应更新过後的 Immutable value 。 -
op:执行的 Operation 资料 。
还有一个 options.affinity ,我们一样在後续遇到它的使用情境时再介绍它的功用
/**
* Transform a point by an operation.
*/
transform(
point: Point,
op: Operation,
options: { affinity?: 'forward' | 'backward' | null } = {}
): Point | null {
return produce(point, p => {
const { affinity = 'forward' } = options
const { path, offset } = p
// ... Point.transform implementation
});
}
insert_node & move_node
因为不会异动到 offset 的值所以实作上非常的 simple ,就只是呼叫 Path.transform 把参数都丢进去而已。
case 'insert_node':
case 'move_node': {
p.path = Path.transform(path, op, options)!
break
}
insert_text
如果 path 与 op.path 为同一路径,且 op.offset 小於等於 offset ,则代表插入的文字位於欲更新的 Point 之前,因此将 p.offset 增加 op.text 的长度。
case 'insert_text': {
if (Path.equals(op.path, path) && o <= offset) {
p.offset += op.text.length
}
break
}
merge_node
当 op.path 与 path 为同一个路径时,将 position 加进 offset 里,再将 path 丢入 Path.transform
case 'merge_node': {
if (Path.equals(op.path, path)) {
p.offset += op.position
}
p.path = Path.transform(path, op, options)!
break
}
remove_text
要移除的文字 op.offset 位於 offset 之前,代表删除的文字位於欲更新的 Point 之前,因此扣除掉两个 offset 之间的长度,最长扣除到 op.text 的长度
case 'remove_text': {
if (Path.equals(op.path, path) && op.offset <= offset) {
p.offset -= Math.min(offset - op.offset, op.text.length)
}
break
}
remove_node
如果 op.path 与 path 为相同路径,或为它的祖先,则直接设为 null ,否则则丢入 Path.transform
case 'remove_text': {
if (Path.equals(op.path, path) && op.offset <= offset) {
p.offset -= Math.min(offset - op.offset, op.text.length)
}
break
}
split_node
我们能先区分成两种情形: op.path 与 path 是否为相同的路径,如果不同则不会异动到 offset value ,直接将 path 丢入 Path.transform 就好
case 'split_node': {
if (Path.equals(op.path, path)) {
// Implementation
} else {
p.path = Path.transform(path, op, options)!
}
break
}
}
这里的 options.affinity 用途与 Path 段落介绍的 split_node 里的一样,代表着节点向後( Forward )或向前( Backward )做拆分。
如果是预设的向後拆分则将在其前面被拆走的 offset 扣掉并一样丢入 Path.transform
if (op.position === offset && affinity == null) {
return null
} else if (
op.position < offset ||
(op.position === offset && affinity === 'forward')
) {
p.offset -= op.position
p.path = Path.transform(path, op, {
...options,
affinity: 'forward',
})!
}
affinity: null 在这边做的事情跟 Path.transform 的 null affinity 一样,将与 Operation 操作相同的 Path 或 Point 节点直接移除,回传 null 。但笔者不太确定它的使用情境就是了,一样欢迎下方留言补充!
Range.transform
这里头主要都是针对 affinity 参数的控制,最後将 range 的 anchor 与 focus point 丢入 Point.transform 进行转换并回传新的 Immutable Range :
/**
* Transform a range by an operation.
*/
transform(
range: Range,
op: Operation,
options: {
affinity?: 'forward' | 'backward' | 'outward' | 'inward' | null
} = {}
): Range | null {
// ... affinity statement control
return produce(range, r => {
const anchor = Point.transform(r.anchor, op, { affinity: affinityAnchor })
const focus = Point.transform(r.focus, op, { affinity: affinityFocus })
if (!anchor || !focus) {
return null
}
r.anchor = anchor
r.focus = focus
})
},
这里的 affinity 除了 'forward' 与 'backward' 与前面在 Path 与 Point 提到的用法一样,是决定节点的拆分( split_node )方向之外,还有 'inward' (向内)以及 'outward' (向外)额外两种情形。中间的判断式就是拿来决定 Range 里的 anchor 与 focus point 要分别以哪种 affinity 进行 transform 的
const { affinity = 'inward' } = options
let affinityAnchor: 'forward' | 'backward' | null
let affinityFocus: 'forward' | 'backward' | null
if (affinity === 'inward') {
if (Range.isForward(range)) {
affinityAnchor = 'forward'
affinityFocus = 'backward'
} else {
affinityAnchor = 'backward'
affinityFocus = 'forward'
}
} else if (affinity === 'outward') {
if (Range.isForward(range)) {
affinityAnchor = 'backward'
affinityFocus = 'forward'
} else {
affinityAnchor = 'forward'
affinityFocus = 'backward'
}
} else {
affinityAnchor = affinity
affinityFocus = affinity
}
Operation 章节到这边总算告一个段落了,这个章节的後两篇我们非常深入地去探讨了 Operation 底层的程序码是如何运作的,希望这能让读者在以 slate 为基础开发编辑器时能更清楚在每一个操作的背後,编辑器实际上都是如何更新的。
不要像笔者一开始一样纯粹靠对 api 名称的直觉做开发XD
下一篇开始我们要来探讨 slate 是如何做肮脏标记与完成资料正规化的。
Normalization 在 slate 中也是一个非常重要的功能,它也支援开发者加入自定义的 Normalizing constraints 。
除了探讨其中的运作方式,我们也会介绍有哪些原始存在的 constraints 、他们的存在意义以及如何自定义 constaints 。
明天新的篇章见罗~
>>: TailwindCSS - 价目表卡片实战 - 登入弹窗开发
Day 07. 安装 Zabbix Agent 在 Windows 10
今天要跟大家介绍如何在其他机器上安装Zabbix Agent 进行监控~ 这次选用的 OS 是 Wi...
Day24 - 在 XState 中的阶层式状态 Hierarchical States
还记得我们在 Day 14 的例子吗? 这是一个比较符合现实情境的 Input 元件状态,只有当 i...
Day16 CSS Specificity 样式拍卖会
权重的概念让我联想到拍卖会,HTML元素的样式就像是拍卖会上被竞标的商品,而选择器们就像是竞标的买...
Angular Stock上市个股日成交(一)(Day27)
今天我们要开始实作最後一个页面了,这个页面功能是可以显示上市个股日成交的资讯 还记得我们在Angul...
[ JS个人笔记 ] AJAX & 工作实作—DAY12
定义与说明 Ajax 是「Asynchronous JavaScript and XML」(非同步的...