[2020铁人赛Day28]糊里糊涂Python就上手-Pandas的观念与运用(上)
今日目标
学习了解 Python Pandas 的观念与运用
What is Pandas?
Pandas 是基於 Numpy 开发的模组,该模组是为了解决结构化资料分析而创建的,Pandas纳入了大量函数和一些标准的资料模型,用於资料挖掘和资料分析,同时也提供数资料清洗功能
事前准备
安装与导入 Pandas
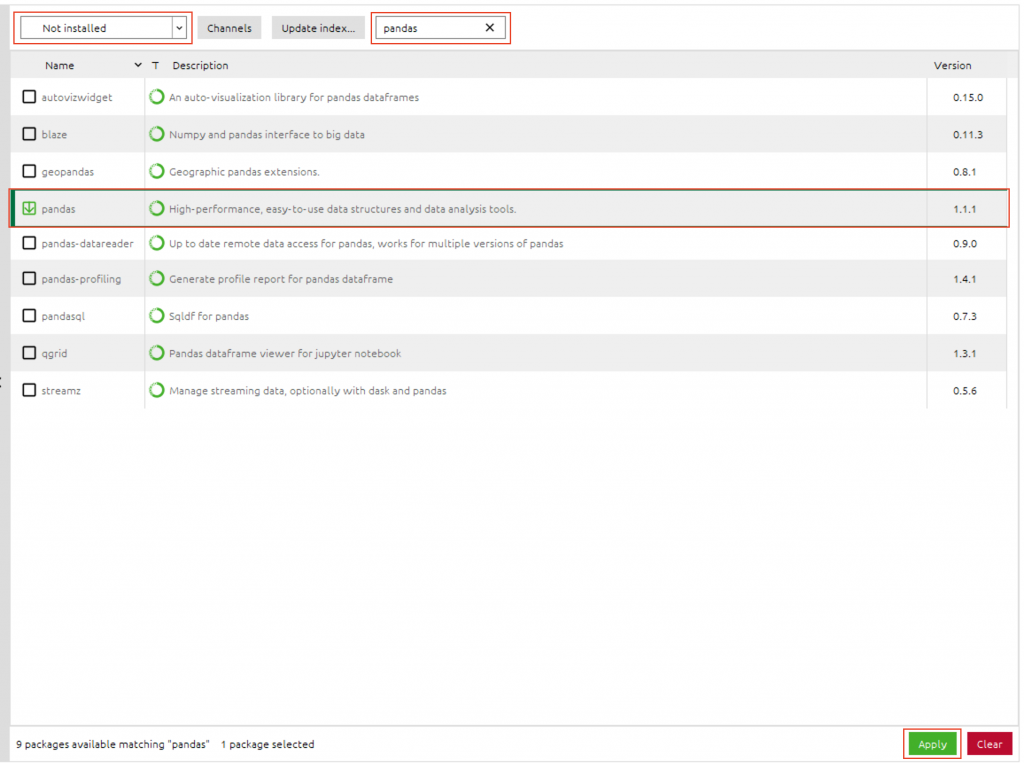
在使用之前需安装与导入 Pandas,可使用 Anaconda 安装:
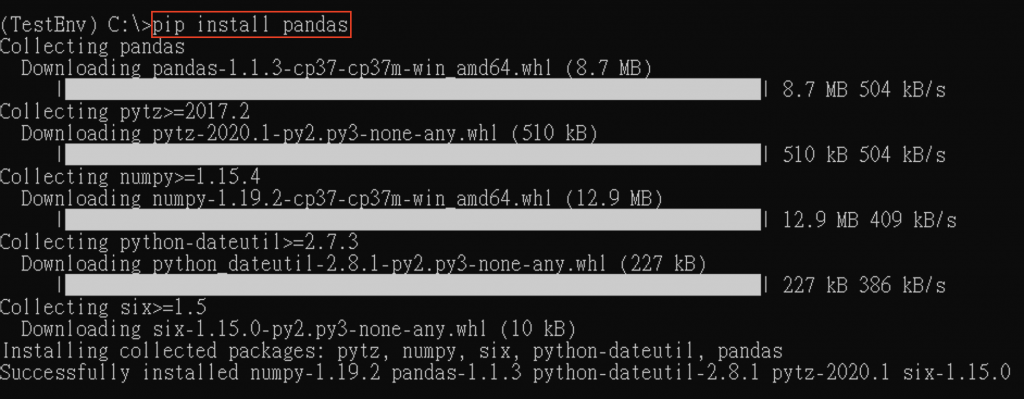
也可使用 pip 安装:
pip install pandas
导入 Pandas 模组:
import pandas as pd
Pandas 观念介绍 & 实际体验
Pandas 资料结构
资料来源可以是串列(List)、元组(Tuple)、字典(Dictionary)、Numpy资料阵列
名称|说明|语法
Series|有索引值的一维资料阵列|pd.Series(资料来源[, index = 自订索引])
DataFrame|有索引值与栏标签的二维资料集|pd.DataFrame(资料来源[, index = 自订索引, columns = 栏位])
Series 实际体验
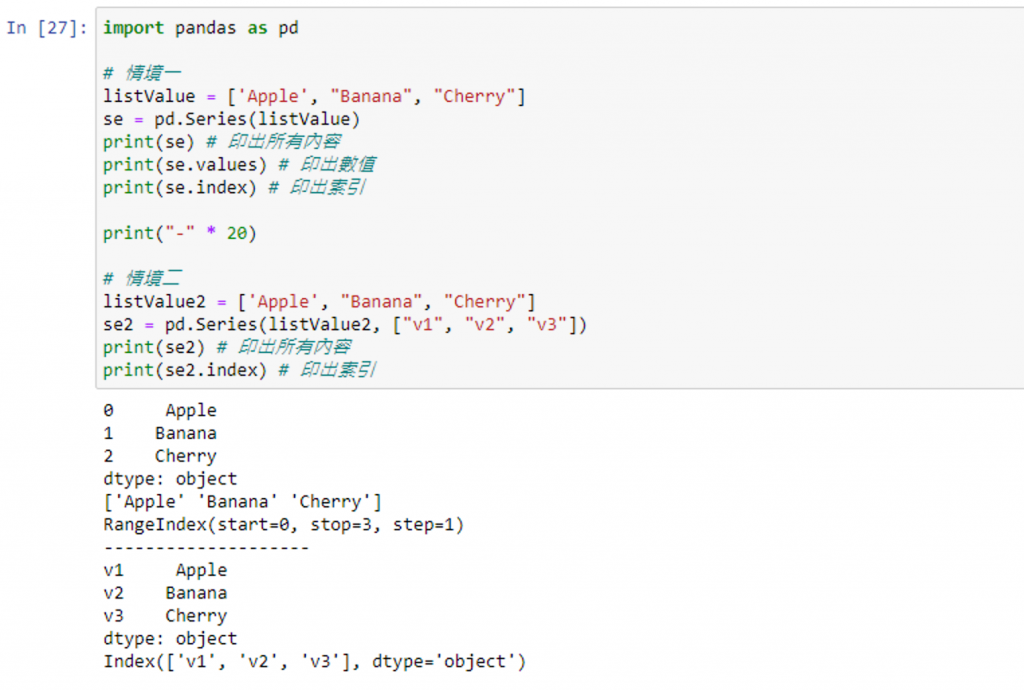
情境一:若是非使用字典的方式,同时未给予自订索引,则 Pandas 会自动给予每个值索引
情境二:若是有给予自订索引,则 Pandas 将会依照给予的索引数值去设定每个值的索引值
完整代码
import pandas as pd
# 情境一
listValue = ['Apple', "Banana", "Cherry"]
se = pd.Series(listValue)
print(se) # 印出所有内容
print(se.values) # 印出数值
print(se.index) # 印出索引
print("-" * 20)
# 情境二
listValue2 = ['Apple', "Banana", "Cherry"]
se2 = pd.Series(listValue2, ["v1", "v2", "v3"])
print(se2) # 印出所有内容
print(se2.index) # 印出索引
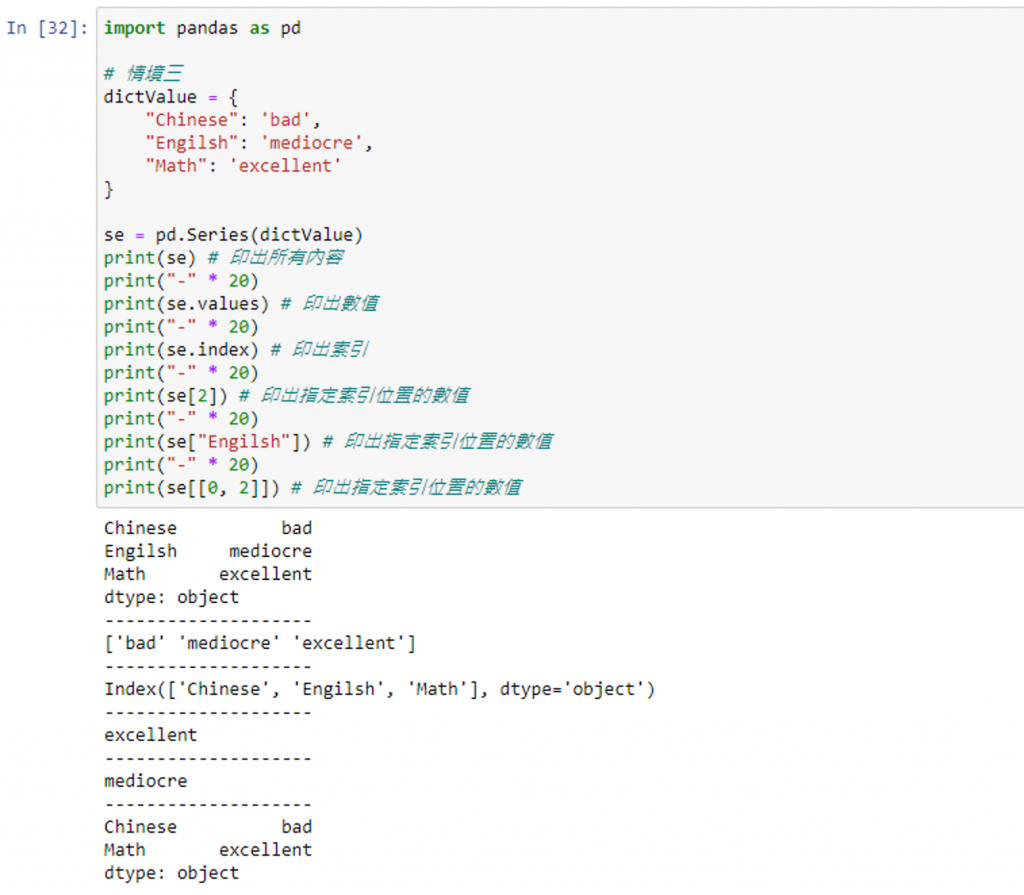
情境三:使用字典当资料来源,去建立 Series,字典的 Key 会是 Series 的索引,而字典的 Value 会是 Series 的资料
完整代码
import pandas as pd
# 情境三
dictValue = {
"Chinese": 'bad',
"Engilsh": 'mediocre',
"Math": 'excellent'
}
se = pd.Series(dictValue)
print(se) # 印出所有内容
print("-" * 20)
print(se.values) # 印出数值
print("-" * 20)
print(se.index) # 印出索引
print("-" * 20)
print(se[2]) # 印出指定索引位置的数值
print("-" * 20)
print(se["Engilsh"]) # 印出指定索引位置的数值
print("-" * 20)
print(se[[0, 2]]) # 印出指定索引位置的数值
DataFrame 实际体验
index 索引是第一列的值,column 是第一栏的栏位名称(若未给予将会预设给予由 0 开始的整数串列)
情境一:未给予 index 值与 column值
情境二:给予 index 值,未给予 column值
情境三:给予 index 值与 column值
完整代码
import pandas as pd
listValue = [
["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"],
["Grape", "Lemon", "Orange"],
["Kiwi", "Pineapple", "Watermelon"]
]
# 情境一:未给予 index 值与 column值
df = pd.DataFrame(listValue)
print(df)
print("-" * 40)
# 情境二:给予 index 值,未给予 column值
df2 = pd.DataFrame(listValue, index=[1, 2, 3])
print(df2)
print("-" * 40)
# 情境三:给予 index 值与 column值
df3 = pd.DataFrame(listValue, index=[1, 2, 3], columns=["v1", "v2", "v3"])
print(df3)

情境四:给予字典并转换数值为 DataFrame,印出 DataFrame 内容
字典的 Key 会是 column,而字典的 Value 里 Key 是 index 索引
完整代码
import pandas as pd
# 情境四
dictValue = {
"Chinese": {"A1":68, "A2":86, "A3":57},
"Engilsh": {"A1":63, "A2":92, "A3":83},
"Math": {"A1":65, "A2":89, "A3":77}
}
df = pd.DataFrame(dictValue)
print(df)
取得 DataFrame 的相关数值
| 取值语法 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|
| df["栏位名称"] | 使用栏位名称取值 |
| df[["栏位名称1", "栏位名称2"...]] | 多个栏位名称取值 |
| df[df["栏位名称"] 条件式] | 以条件式去判定指定的栏位是否符合条件,若是符合则为True,不符合则为False,再藉由判断後的回传值印出符合的所有数值 |
| df["栏位名称"].values | 仅取出指定栏位内的数值 |
| df.values[索引位置] | 取出指定索引的数值 |
| df.columns | 取出栏位名称 |
| df.indes | 取出 index |
| df.describe() | 描述性统计值 |
完整代码
import pandas as pd
dictValue = {
"Chinese": {"A1":68, "A2":86, "A3":57},
"Engilsh": {"A1":63, "A2":92, "A3":83},
"Math": {"A1":65, "A2":89, "A3":77}
}
df = pd.DataFrame(dictValue)
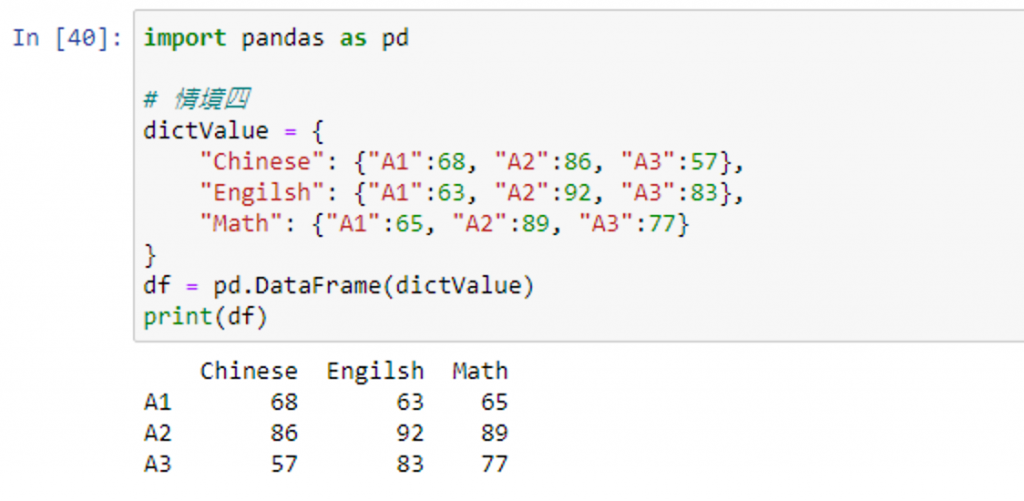
print(df) # 印出所有数值
print("-" * 40)
print("取出 Chinese 的相关数值:\n", df["Chinese"]) # 印出 Chinese 的相关数值
print("-" * 40)
print("取出 Chinese Math 的相关数值:\n", df[["Chinese", "Math"]])# 印出 Chinese Math 的相关数值
print("-" * 40)
print("取出以 Chinese 为基准,取其中及格(>=60)的所有相关数值:\n", df[df["Chinese"] >= 60]) # 印出以 Chinese 为基准,取其中及格(>=60)的所有相关数值
print("-" * 40)
print("仅取出 Chinese 的数值:\n", df["Chinese"].values) # 印出仅取出 Chinese 的数值部分
print("-" * 40)
print("仅取出 A1 的 Engilsh 的数值:\n", df.values[0][1]) # 印出仅取出 A1 的 Engilsh 的数值
print("-" * 40)
print("取出栏位名称:", df.columns) # 印出栏位名称
print("-" * 40)
print("取出 index:", df.index) # 印出 index
print("-" * 40)
print("印出描述性统计值:\n", df.describe()) # 印出描述性统计值
执行後结果为:
| 取值语法 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|
| df.loc["索引名称", "栏位名称"] | 以索引名称及栏位名称取得资料 |
| df.iloc["索引编号", "栏位编号"] | 以索引编号及栏位编号取得资料(资料起始为0) |
| df.head(n) | 取得最前面的指定笔数资料,n 为选择性填写参数,若不填写则取得最前面 5 笔资料 |
| df.tail(n) | 取得最後面的指定笔数资料,n 为选择性填写参数,若不填写则取得最後面 5 笔资料 |
完整代码
import pandas as pd
dictValue = {
"Chinese": {"A1":68, "A2":86, "A3":57},
"Engilsh": {"A1":63, "A2":92, "A3":83},
"Math": {"A1":65, "A2":89, "A3":77}
}
df = pd.DataFrame(dictValue)
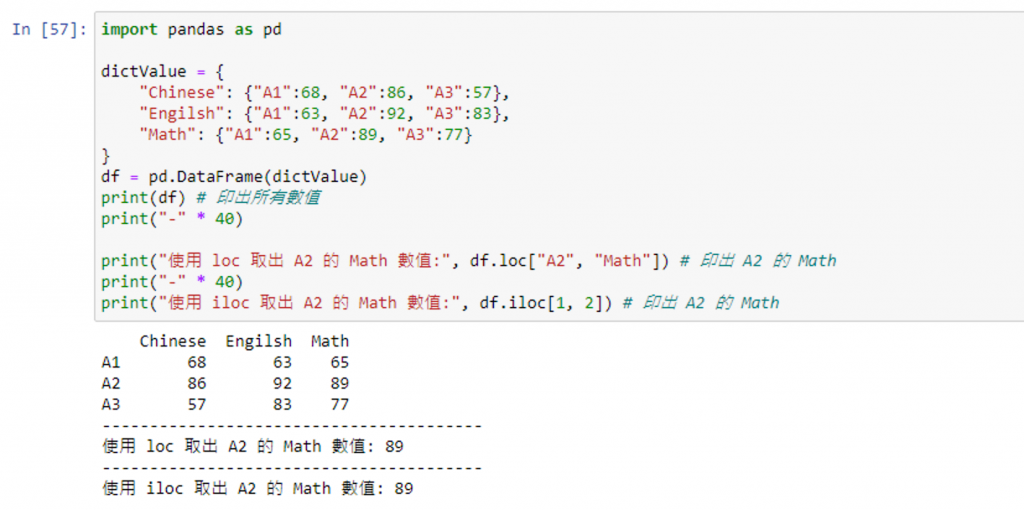
print(df) # 印出所有数值
print("-" * 40)
print("使用 loc 取出 A2 的 Math 数值:", df.loc["A2", "Math"]) # 印出 A2 的 Math
print("-" * 40)
print("使用 iloc 取出 A2 的 Math 数值:", df.iloc[1, 2]) # 印出 A2 的 Math
结论
以上为 Python Pandas 资料结构的简易说明,将在下篇正式进入到 Pandas 存取档案资料与运用视觉化呈现数据
Day22 Let's ODOO: 继承Model来增加栏位
今天我们来示范透过继承Model来新增Field和更改Views里面的属性,用这种方法可以省去自己建...
JavaScript 概述
完整的javascript包含: 1.ECMAScript,描述该语言的语法和基本物件。 2.文件物...
Day 26. 双向绑定语法糖 - v-model
表单输入绑定 我们可以用v-model指令在表单<input>、<textarea...
[Day 18] 第一主餐 pt.10-中文资料存料至文中,django如何存取中文
前一篇我们把资料库修改完成了 今天我们就要来把BeautifulSoup的中文资料送过去了 由於昨天...
[3D地图-CesiumJS系列] 三、车辆废气排放地图 - 以粒子系统(Particle system)实作
本篇文章请搭配 [3D地图-CesiumJS系列] 一、快速上手 [3D地图-CesiumJS系列]...