30天学习笔记 -day 24-Dagger (下篇)
今天会补充dagger的用法。
今天目标:一个 Acomponent 里放着 Fruit.class 的依赖实例,另一个Bcomponent里放着 Fruitshop.class 的依赖实例,Acomponent 公开Fruit的依赖实例让 Bcomponent 也能获取。
建立Fruit.Class
public class Fruit {
private String name;
private String price;
public Fruit(String name,String price){
this.name=name;
this.price=price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(String price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
建立Fruitshop.class
Constructor放入两个string类型(水果店名称、电话)、一个Fruit类型(水果)
public class FruitShop {
private String fruitShopName;
private String shopPhone;
private Fruit fruit;
public FruitShop(String fruitShopName, String shopPhone,Fruit fruit){
this.fruitShopName=fruitShopName;
this.shopPhone=shopPhone;
this.fruit=fruit;
}
//getter&&setter
public String getFruitShopName() {
return fruitShopName;
}
public void setFruitShopName(String fruitShopName) {
this.fruitShopName = fruitShopName;
}
public String getShopPhone() {
return shopPhone;
}
public void setShopPhone(String shopPhone) {
this.shopPhone = shopPhone;
}
public Fruit getFruit() {
return fruit;
}
public void setFruit(Fruit fruit) {
this.fruit = fruit;
}
}
自定义scope
Scope跟@Singleton一样都是单例模式,被@Scope注解所标识的Component的生命周期内,只要是@Scope所标识提供依赖的方法,那麽所提供的依赖都是单例!
这次自订义两种scope:FruitScope跟FruitShopScope,除了命名不同其他都一样
@Documented
@Scope
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface FruitScope {
}
Fruit2Module
将Component 提供在Module,
Fruit2Module的部分在提供Fruit的地方加上@FruitScope
@Module
public class Fruit2Module {
private String name;
private String price;
//constructer
public Fruit2Module(String name,String price){
this.name=name;
this.price=price;
}
@Provides
@FruitScope
Fruit provideFruit(@Named("name")String name, @Named("price")String price){
return new Fruit(name,price);
}
@Provides
@Named("name")
String provideFruit1Name(){
return name;
}
@Provides
@Named("price")
String provideFruit1Price(){
return price;
}
}
Fruit2Component
module里provide方法有@FruitScope则使用该Module的Component也需要@FruitScope。
@FruitScope
@Component(modules = Fruit2Module.class)
public interface Fruit2Component {
void inject(TestApplication testApplication);
//提供给其他Component使用
Fruit getFruit();
}
Fruit getFruit();将Fruit提供给其他有依赖关系的Component
FruitShop1Module
将Component 提供在Module,
在FruitShop1Module提供的provideFruitShop中加入@FruitShopScope
@Module
public class FruitShop1Module {
private String fruitShopName;
private String shopPhone;
//Constructor
public FruitShop1Module(String fruitShopName,String shopPhone){
this.fruitShopName=fruitShopName;
this.shopPhone=shopPhone;
}
@Provides
@FruitShopScope
FruitShop provideFruitShop(@Named("ShopName")String fruitShopName,@Named("shopPhone")String shopPhone, Fruit fruit){
return new FruitShop(fruitShopName,shopPhone,fruit);
}
@Provides
@Named("ShopName")
String provideFruitShopName(){
return fruitShopName;
}
@Provides
@Named("shopPhone")
String provideFruitShopPhone(){
return shopPhone;
}
}
FruitShop1Component
module里provide方法有@FruitShopScope则使用该Module的Component也需要@FruitShopScope。
@Component注解中加入使用的modules跟依赖的Component,就可以拿到Fruit2Component提供的功能。
@FruitShopScope
@Component(modules = FruitShop1Module.class,dependencies = Fruit2Component.class)
public interface FruitShop1Component {
void inject(Test2Activity activity);
}
TestApplication.class
build之後就可以使用DaggerFruit2Component
public class TestApplication extends android.app.Application {
private Fruit2Component fruit2Component;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
fruit2Component= DaggerFruit2Component.builder()
.fruit2Module(new Fruit2Module("柚子","30"))
.build();
fruit2Component.inject(this);
}
//将fruit2Component返回
public Fruit2Component getFruit2Component(){
return fruit2Component;
}
}
这里要注意!!
要在manifest加上android:name=".加上自定的Application",不然dagger会报错
Test2Activity
@InjectFruitShop会自动赋值。
public class Test2Activity extends AppCompatActivity {
private FruitShop1Component fruitShop1Component;
@Inject
FruitShop fruitShop;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_test2);
fruitShop1Component=DaggerFruitShop1Component.builder()
.fruitShop1Module(new FruitShop1Module("123水果店","0x00000000"))
//拿到TestApplication中getFruit2Component()
.fruit2Component(((TestApplication)getApplication()).getFruit2Component())
.build();
fruitShop1Component.inject(this);
Log.d("fruit", fruitShop.getFruit().getName());
Log.d("fruitshop",fruitShop.getFruitShopName());
}
}
Log回传:
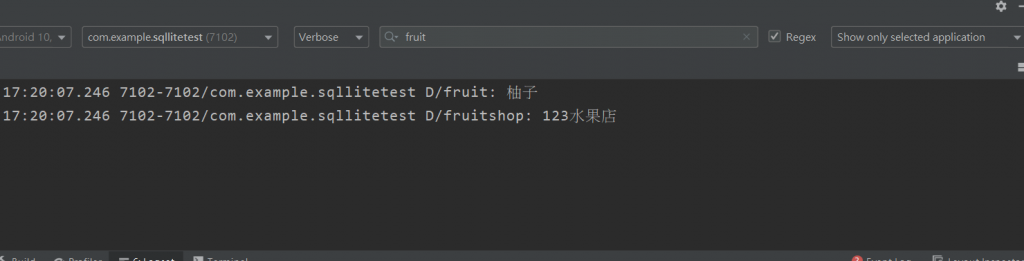
注意事项:
1.被依赖的component必须将需要的依赖实例暴露出来,其他有依赖关系的component才能被提供。
2.依赖关系中的component不能拥有相同的SCOPE,会因为生命周期不同而报错。
以上就是今天的内容。
>>: Day27 - 动态模型 part2 (LSTM with attention)
Day-24 Thread
Thread tags: IT铁人 虽然前面说CPU在执行程序时,都用process来叙述,不过其实...
Day11 职训(机器学习与资料分析工程师培训班): Python程序设计, 建立Model+载入
上午:Python程序设计 早上学习function, *args, *kwargs, 全域变数 &...
Day11 X Lazy Loading
还记得昨天 Virtualized List 篇章开头放的 Facebook demo 影片吗?有...
第28天:箭头函式与this()
在解析this的方式箭头函式与函式宣告不同,函式宣告是以呼叫时的方式来决定,而箭头函式在建立时就会决...
D19 - 「呐,你想要成为什麽颜色?」:打造一个调色盘吧!
接下来我们要利用「 PWM」与「RGB LED」设计调色盘功能。 首先来认识一下新朋友 - 「RGB...